What are spacecrafts?
Spacecrafts are vehicles designed for space travel with or without a crew, in a controlled flight pattern, used by large space agencies such as NASA, CNES, ESA, SpaceX, etc.
How do spacecrafts work?
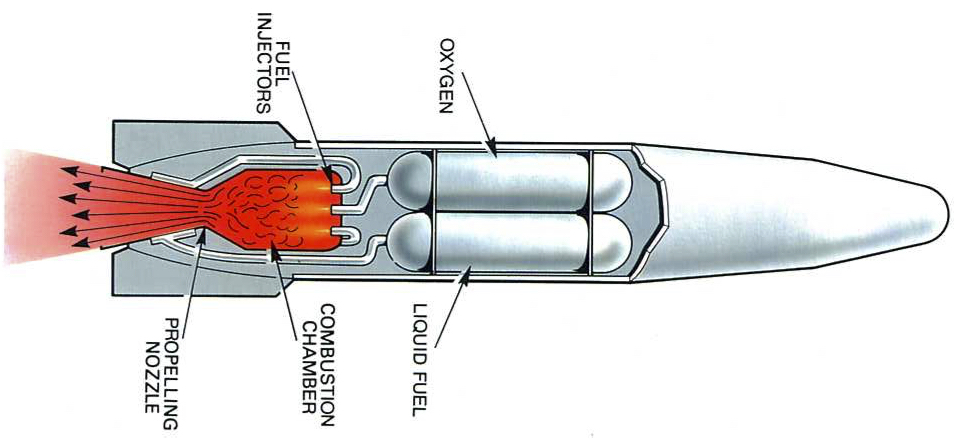
- Spacecrafts work by generating thrust in a controlled explosion using a violent chemical reaction between fuel and oxygen inside a combustion chamber. The expanding gases from the explosion are pushed out the bottom of the craft, through a nozzle. The rocket then moves forward due to the concentrated thrust force coming out of the nozzle.
- When the rocket has enough momentum to stay up in space, the combustion chambers detach from the spacecraft, and usually land back on earth to be reused.
International Space Station (ISS)
The International Space Station (ISS), is a large space station assembled and maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA (Japan), ESA (Europe), CSA (Canada). The ISS is the largest space station ever built. Its primary purpose is performing microgravity and space environment experiments.
- The station’s design was developed between 1984 and 1993.
- The ISS orbits approximately 435 kilometres above Earth’s surface. Its elevation (snow height) is officially recognized as 8,848.86 metres above sea level.
- The station celebrates its 20th anniversary since the launch of its first element, Zarya, in November 2018.
- Over 270 astronauts from various countries have visited the ISS during its 25 years in orbit.
Spacecraft Evolution
Spacecrafts have evolved greatly in the last 80 years. From the Sputnik 1, the first satellite in space, to the starship that can land itself, space travel has greatly impacted the field of space transportation, and will continue to.
Propulsion systems on spacecrafts have greatly changed. Take the Saturn V for example; the most powerful spacecraft in history that was able to bring humans to the moon during the 1969 Apollo 11 mission. When talking about newer spacecraft, the Falcon 9 from SpaceX also shows great power, as well as reliability. New spacecrafts are also able to autonomously land themselves. With spacecrafts having lots of changes in a short period of time, it's unclear how far technology can go.
See more - Saturn V
Challenges of Space Travel
Even though space travel is an exciting and insightful topic, there are bound to be issues and risks, including radiation exposure, muscle atrophy, and extreme temperatures, etc. Overcoming these challenges necessitates new ways of building spacecrafts and spacesuits, as well as using new technologies.
Space Travel's Impact on Society
Space travel can have an immense impact on society. This is because the concept may alter the though process of future innovations. It also opens new working fields, and informs the general public about topics beyond Earth.
Famous Spacecrafts (Click to view)
Below are some famous spacecrafts from various countries known for their accomplishments.
References
Blogspot. (n.d.). Blogspot. Retrieved May 24, 2024, from
https://shayne-mckee.blogspot.com/2021/05/rocket-science-101-operating-principles.html
BlueOrigin. (n.d.). BlueOrigin. Blue Origin: Home. Retrieved May 24, 2024, from
https://www.blueorigin.com/
Harland, D. M. (n.d.). Spacecraft | Definition, Types, & Facts. Britannica. Retrieved May 24, 2024, from
https://www.britannica.com/technology/spacecraft
Nasa. (n.d.). Nasa.Gov. Retrieved May 24, 2024, from
https://www.nasa.gov/wp-content/uploads/2012/03/rockets-guide-20-how-rockets-work.pdf?emrc=65f9a5b9048ff
Nasa. (n.d.). Wikipedia. Retrieved May 24, 2024, from
https://www.nasa.gov/?search=iss
SpaceX. (n.d.). SpaceX. SpaceX. Retrieved May 24, 2024, from
https://www.spacex.com/

